Realized Volatility
Realized Volatility
For any price feed, Pragma offers a realized volatility feed. The realized volatility feed uses checkpoints to calculate the annualized volatility of an asset over a period of time.
Sample Code
If you are just trying to get started with our realized volatility feed, see this self-contained code snippet here. You can find the full Oracle interface specification is available here.
BTC/USD 1 week Realised volatility
use starknet::ContractAddress;
use pragma_lib::abi::{
ISummaryStatsABIDispatcher, ISummaryStatsABIDispatcherTrait
};
use pragma_lib::types::{AggregationMode, DataType};
use starknet::get_block_timestamp;
use starknet::contract_address::contract_address_const;
fn compute_volatility(data_type: DataType, aggregation_mode: AggregationMode) -> u128 {
let SUMMARY_STATS_ADDRESS: ContractAddress =
contract_address_const::<0x6421fdd068d0dc56b7f5edc956833ca0ba66b2d5f9a8fea40932f226668b5c4>();
let start_tick = starknet::get_block_timestamp() - 604800;
let end_tick = starknet::get_block_timestamp();
let num_samples = 200;
let summary_dispatcher = ISummaryStatsABIDispatcher { contract_address: SUMMARY_STATS_ADDRESS };
let (volatility, decimals) = summary_dispatcher
.calculate_volatility(data_type, start_tick, end_tick, num_samples, aggregation_mode);
return volatility; // will return the volatility multiplied by 10^decimals
}
//USAGE
let pair_id = 18669995996566340; //felt252 conversion of "BTC/USD"
//SPOT
let volatility = compute_volatility(DataType::SpotEntry(pair_id), AggregationMode::Median(()));
How Realized Volatility is Calculated
We compute realized volatility under the Geometric Brownian Motion assumption using the following equation:
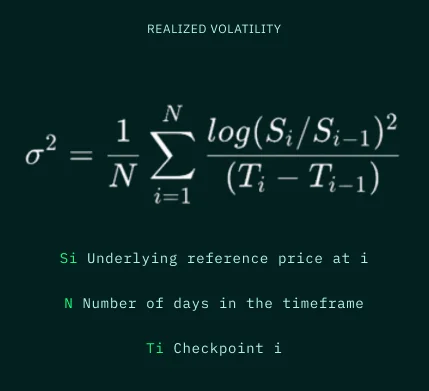
Where σ is in units of 1/$\sqrt{T}$. We then multiply σ by $\sqrt{ΔTyear}$ to get the annualized volatility of the underlying asset.
Technical Specification
Function: calculate_volatility
This function allows you to query realized volatility for any price feed calculated over a requested period of time. The function accesses checkpoints within the requested timeframe, and uses the above equation to calculate realized volatility.
Currently, Pragma sets a checkpoint every 5 minutes. If you need more granular data, you can set more checkpoint via the set_checkpoint function.
Inputs
data_type: enum of the data type you are requesting (See DataType structure). By providing the enum data type, you also provide the pair id (for spot entries), or the pair id and the expiration timestamp (for futures)start_tick: timestamp at the beginning of the period over which you want to calculate realized volatilityend_tick: timestamp at the end of the period over which you want to calculate realized volatility. If set to 0, it defaults to the timestamp of the last published blocknum_samples: number of samples on which you want to calculate volatility. Starknet currently limits computation, so there is a max of 200 for this inputaggregation_mode: aggregation mode to use for combining the many data sources available in Pragma. Use the structure AggregationMode defined in Pragma. Option must currently be set toMEDIAN,MEANorCONVERSIONRATE. Additional optionsVWAP,EXPONENTIAL_DECAYare coming soon.
Returns
volatility: annualized realized volatility percentage. Volatility is reported with 8 decimals of precision. To convert it to percentage, divide the output by 10^8 (e.g. 7076538586 means annualized volatility is around 70%)decimals: number of decimals, i.e. , the number of places that value has been shifted to allow for greater accuracy.